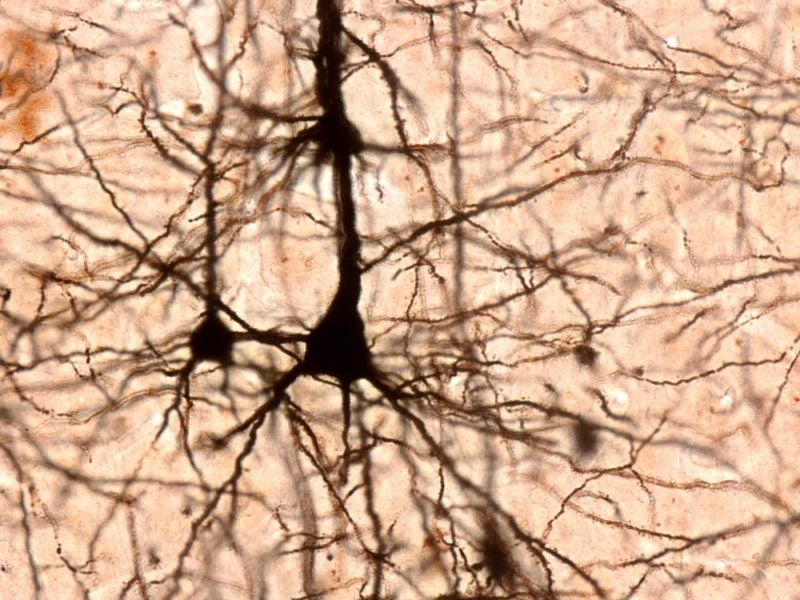
Swiss Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)’s Blue Brain Project has used a mathematical algorithm to distinguish the shape and structures of pyramidal cells.
The project has classified 17 cells in rat somatosensory cortex. This will allow a better understanding of cell taxonomy and of the brain’s components and their functions.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
A catalogue of neurons can also be used to map the function and role in disease of every type of neurons in the brain. Lack of understanding of the biology of neurological and neurodegenerative conditions is the main barrier to creating new treatments and cures for these conditions.
Pyramidal cells comprise 80% of the neurons in the neocortex and collect information from other neurons throughout the brain. Scientists have disagreed about whether the objective classification of these neurons is possible at all.
Founder and director of the Blue Brain Project Professor Henry Markram said: “For nearly 100 years, scientists have been trying to name cells. They have been describing them in the same way that Darwin described animals and trees. Now the Blue Brain Project has developed a mathematical algorithm to objectively classify the shapes of the neurons in the brain.
“This will allow the development of a standardized taxonomy [classification of cells into distinct groups] of all cells in the brain, which will help researchers compare their data in a more reliable manner.”

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThe algebraic topology-based machine learning algorithms used in the project were developed by EFPL professor Kathryn Hess with University of Aberdeen’s Ran Levi.
To classify the neurons, their tree-like structure is transformed into a barcode, which can be input into an algorithm to classify the neurons into distinct group.
Lead scientist at the Blue Brain Project Lida Kanari said: “The Blue Brain Project is digitally reconstructing and simulating the brain, and this research provides one of the solid foundations needed to put all the types of neurons together.
“By removing the ambiguity of cell types, the process of identifying the morphological type of new cells will become fully automated.”




