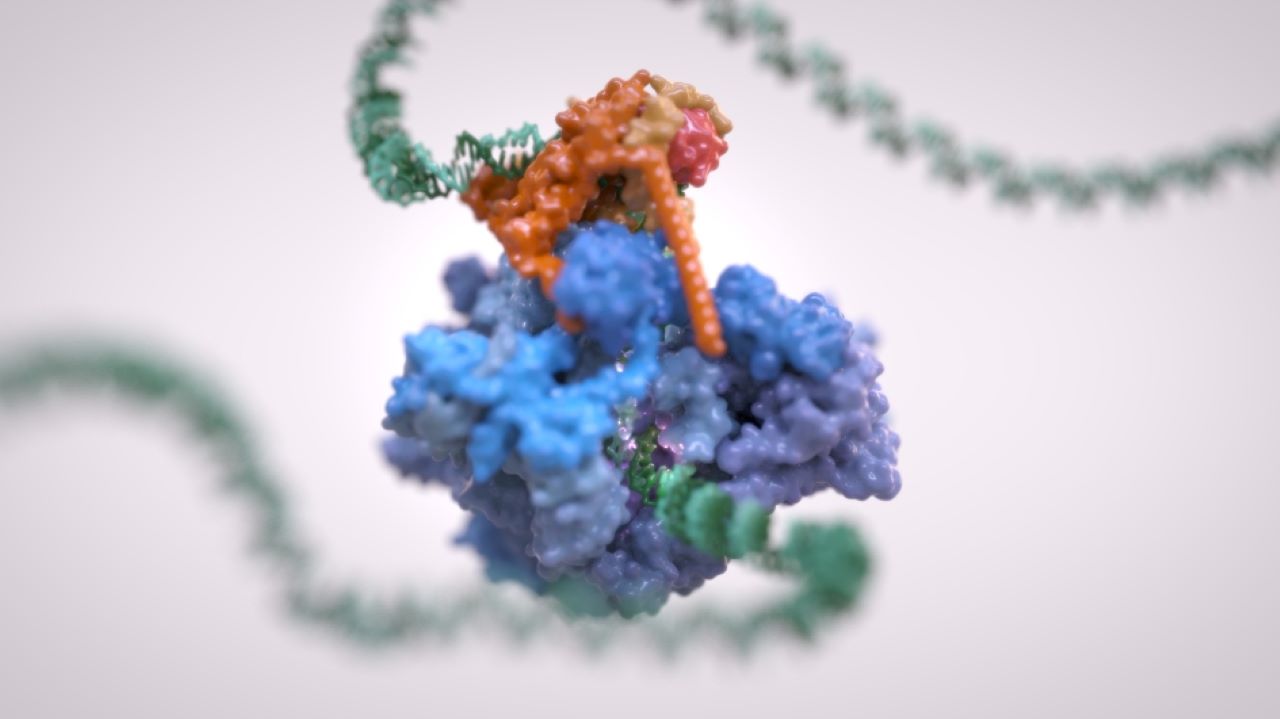
The UK Institute of Cancer Research, London (ICR) researchers have created a three-dimensional (3D) structure of a complex of molecules for new therapies.
Scientists noted that the structure, which also has links to cancer, plays a fundamental role in life and could cause increased sensitivity to viral infections, as well as neurodegenerative diseases.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
Known as RNA polymerase III (Pol III), the protein complex reads DNA to decode housekeeping genes and aids in creating the proteins that form the basic building blocks of cells.
Cancer cells often hijack this process to stimulate their rapid growth and division, the scientists noted.
According to scientists, cancer cells use Pol III to keep them fuelled with the protein building blocks needed for rapid growth and division. Furthermore, mutations in Pol III can also cause neurodegenerative disease in humans.
Three years ago, the ICR scientists unveiled the structure of Pol III in yeast. Now, the team working with colleagues in Germany revealed the 3D structure of the human version of the protein complex.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThey also mapped the precise structural effects of various disease mutations connected with neurodegeneration and increased sensitivity to infection by viruses.
This could pave a path for efforts targeting the protein complex with new drugs, the study, funded by Wellcome and Cancer Research UK, found.
The Institute of Cancer Research, London Integrative Structural Biology professor and study leader Alessandro Vannini said: “The Pol III protein complex is fundamental to life – decoding our DNA and ensuring our cells can build the proteins they need to grow and divide. And we believe it could have a role in the development of cancer.
“Our findings provide a vivid, extremely detailed three-dimensional map of Pol III, showing the structure of its various active sites, and how these are affected by various mutations linked to neurodegenerative diseases and viral infections.
“We hope our work can act as a 3D treasure map for the future discovery of new treatments targeting the Pol III complex.”




