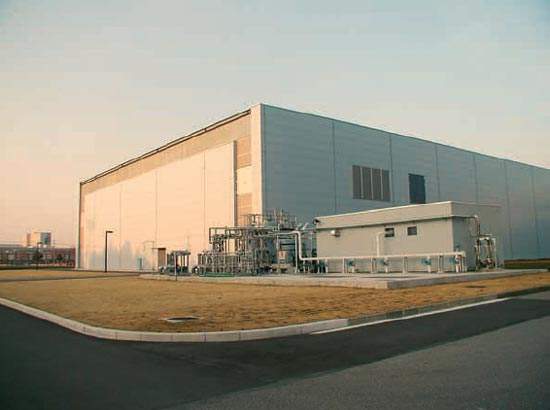
Chugai Pharmaceutical opened the first phase of its antibody production facility in Utsunomiya, Japan, in early 2004, following FDA approval along with validation and cGMP requirements being satisfied.
The second phase of the construction has also been completed, and includes the addition of more bioreactor capacity than the original plan called for. A third injection products building has also been constructed.
In late February 2005, the company decided to streamline their operations by integrating their existing five domestic plants into two at Utsunomiya and Fujeida. This meant that the 21.9ha (54 acre) Utsunomiya plant would have become their main facility for bulk production and the formulation of biopharmaceuticals.
However, the restructuring plan was amended in November 2007, cancelling the closure of the Ukima plant in Kita-ku, Tokyo, due to the potential of manufacturing bulk biopharmaceuticals in the current facilities. A three plant production system including Ukima, Utsunomiya and Fujieda plant was suggested instead.
Chugai operates three plants: Ukima, Utsunomiya and Fujideda. A fourth plant in Kamakura was closed in December 2010.
The total capital investment for phases one and two of the Utsunomiya facility amounted to some 14.96bn yen: 5.6bn yen for phase one and 9.36bn yen for phase two.
The Utsunomiya plant is the production hub for antibody drugs, and has the largest domestic animal cell culture facility. Solid-form drugs production has been relocated from the Ukima and Kamakura plants and integrated into the Fujieda plant, which operates as an intensive plant for synthetic drugs.
The Utsunomiya plant was damaged by the major earthquake that hit the Pacific Coast of Tohoku on 11 March 2011. Investigations on the extent of damage and the time required for recovery are under way, certain functions were resumed on 16 March 2011.
Contractors and timelines: phase one
Hitachi began construction of phase one of the antibody production facility in February 2001; building work was completed in January 2002 and the plant was fully equipped and outfitted by March 2003. The phase one facility commenced operations in January 2004, following final commissioning and validation. Hitachi provided the engineering, procurement, construction and validation services complying with cGMP.
The phase one facility had 8,600m² of floor space, and was outfitted with two 10,000l bioreactors for experimental scale production of monoclonal antibody therapies. The first phase also included extensive preparation facilities, inoculation suite, media preparation, culture preparation tanks, downstream processing and separation suites.
The company’s clinical trial / pre-commercial facilities included the two 10,000l bioreactors and two 2,500l bioreactors at the Ukima plant in Tokyo.
Contractors and timelines: phase two
The phase two facility was constructed as a major commercial pharmaceutical production facility. Hitachi began construction in May 2003, and it was completed by January 2004. Amersham Biosciences supplied an integrated processing system that included BioProcess systems, Chromaflow columns, affinity media (Protein A Sepharose) and ultrafiltration modules, and also carried out some validation work.
The equipping and outfitting of the antibody production plant was complete by the second quarter of 2005. The floor space of the phase two facility is 4,020m². The facility has six 10,000l bioreactors installed along with associated media, culture and inoculation preparation facilities. Phase two shares some of the infrastructure of the phase one facility.
Chugai upgraded its plans for the phase two facility in October 2003 by increasing the number of bioreactors intended from four to six.
Products and partners
The Utsunomiya plant now produces several products including Epogin pre-filled syringes, Neutrogin (Granocyte), Epoetin Beta (recombinant erythropoietin) and Lenograstim.
The phase two antibody facilities are producing Actemra (also known as MRA), a humanised anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, which has been approved as a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. In 2003, Chugai Pharmaceutical and Roche agreed to jointly develop and promote the drug. It has since been approved for other indications, such as Castleman’s disease.
MRA was approved for Phase III clinical trials for rheumatoid arthritis in Japan in 2008. the drug was approved in Europe (where it is marketed as RoActemra) in January 2009, and in the US in 2010. Chugai developed the treatment through a strategic alliance with Hoffmann-La Roche (agreed in 2002). The Utsunomiya plant serves as one of the largest potential commercial suppliers of these treatments.