Fraunhofer CMB opened a new cGMP plant-based vaccine facility in Newark, Delaware, in April 2010. The facility is a partnership between Fraunhofer’s two centres (the Center for Molecular Biotechnology (CMB) in Newark, Delaware and the Center for Manufacturing Innovation (CMI) in Boston, Massachusetts), the Boston University College of Engineering and iBio, a Newark-based biopharmaceutical company.
This first-of-its-kind facility develops vaccines and therapeutics using natural green plants. Fraunhofer CMB developed the plant-based system over a period of eight years including a three year collaboration between Boston University and the two centres of Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Europe’s largest applied research organisation.
The $15m facility is expected to play a crucial role in addressing and containing future pandemics and emerging biological threats.
Construction of the facility was completed in 2009 and validation took place in 2010. The facility is equipped for rapid and cost-effective production of vaccines in comparison to the traditional method of vaccine production.
Fraunhofer vaccine facility
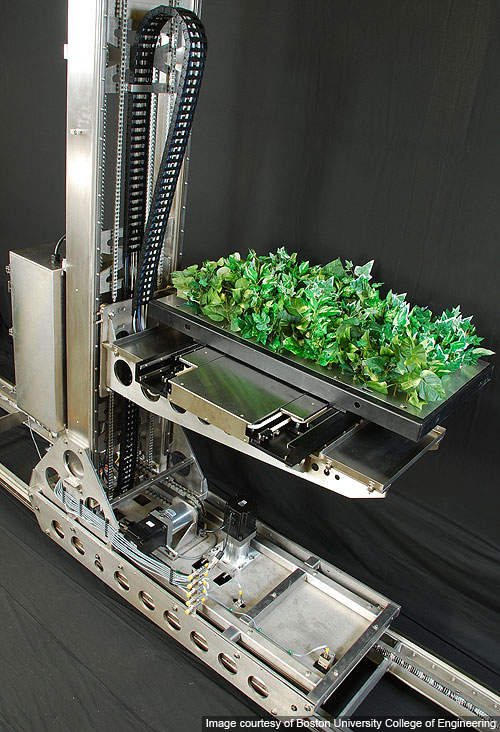
The facility is 13,000ft² and is located on the first floor of CMB’s 56,000ft² building in Newark, Delaware. Designed to be cost, time and space efficient, the facility is fully automatic and houses lighted, irrigated growth modules and processing stations.
It is equipped with Fraunhofer CMI designed, robotically operated, custom engineered machines (including seeding and harvesting machines) and specially designed multi-plant trays. The robots execute all the operations within the facility.
Production
The facility produces large quantities of vaccines and therapeutics using natural green plants that are not genetically modified. Specific proteins are produced from tobacco plants.
The material for the first human clinical trial of plant-produced H5N1 influenza vaccine that began in September 2010 was produced at the facility.
The facility has the capacity to grow tens of thousands of plants in a single batch.
Technology
The facility uses Fraunhofer CMB’s proprietary viral vector technology developed by the company for iBio. Using the technology, host plants are hydroponically grown in multi-plant trays. A seeding machine separates picks and plants the seeds on the growth trays into an array pattern. To facilitate recirculation of nutrients and allow consistent, optimal growth of biomass, the trays are kept under controlled light and temperature conditions.
The trays are handled and moved around different processing stations within the facility by robots. The robots glide up and down the narrow aisles within the facility. After several weeks of growing, the robots carry the plant trays to a machine where all aerial parts of the plants are vacuum-infiltrated with agrobacterium carrying expression vectors.
Through virus replication, the viral sequence of the expression vectors amplifies with the clones target sequences resulting in production of a target protein. Following several more weeks of growing, the target is accumulated in the plant tissue within leaves.
Before downstream processing is carried out, the robots take the plant to a harvesting machine for biomass harvesting. The harvesting machine removes the plants from their respective trays and the protein is purified and extracted following a routine chemical separation procedure.
Unlike traditional vaccine production methods, the facility completes the entire process of vaccine production from seeding to harvesting within a span of six weeks. The recovery of large doses of bulk drug substance is completed within two weeks from the time when the plants reach a certain growth stage. Due to complete automisation, any potential process contamination caused by human contact is also eliminated.
Finance
The facility has been financed through state and private funding. The state of Delaware granted $5m. The remaining $10m was sourced internally from Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency sanctioned $4.4m under the Accelerated Manufacturing of Pharmaceuticals programme to support phase I trials of H1N1 flu vaccine manufactured at the facility.