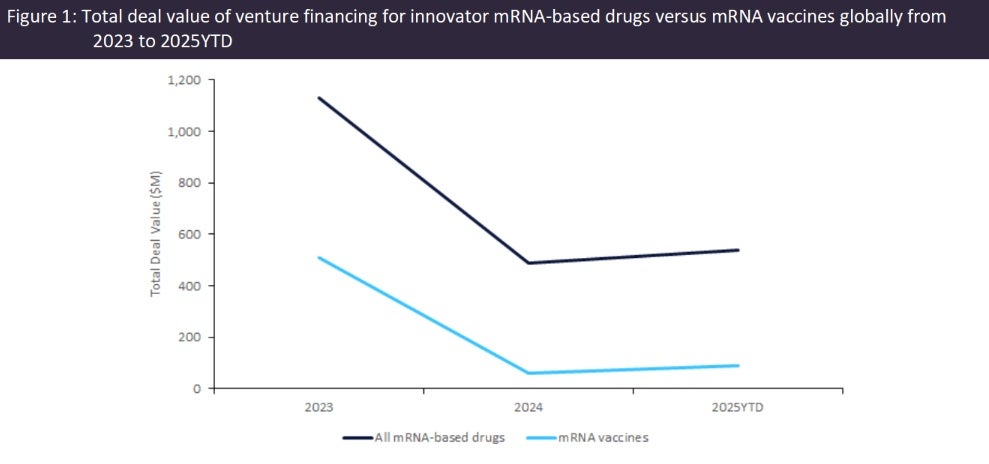
Venture financing for messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based innovator vaccines declined by 82% from $510m in 2023 to $90m in the 2025’s year to date (YTD), according to GlobalData’s Pharma Intelligence Center Deals Database. Biotech companies developing mRNA-based vaccines face uncertainty as the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) – led by health secretary Robert F Kennedy (RFK) Jr – announced on 5 August 2025 cuts of $500m in grant funding for projects involving the development of mRNA vaccines, stating that they “fail to protect effectively against upper respiratory infections like Covid[-19] and flu”.
mRNA-based drugs, which include vaccines and therapeutics, deliver synthetic mRNA to cells using lipid nanoparticles or other delivery vehicles, resulting in the production of proteins that can prevent or treat disease. The success of mRNA vaccines – notably Pfizer’s Comirnaty and Moderna’s Spikevax – against the Covid-19 pandemic fuelled investor confidence, and spurred efforts to expand mRNA technology into broader therapy areas such as cancers and genetic disorders.
Venture financing for companies developing innovator mRNA-based drugs more than halved from $1.1m in 2023 to $488m in 2024, then recovered slightly to $539m by 2025 YTD (Figure 1). Oncology and infectious diseases were the top therapy areas for venture financing involving mRNA-based drugs, totaling $1.3m and $936m, respectively, over the 2023 to 2025 YTD period. Oncology and infectious diseases also accounted for the largest numbers of mRNA-based drugs in active development, accounting for 32% and 31% of drugs in the discovery and preclinical stages, respectively, and 22% and 65% of those in the combined clinical, preregistration, and marketed stages, according to GlobalData’s Pharma Intelligence Center Drugs Database. However, excluding infectious disease and oncology, 91% of the total mRNA-based drugs remain in the preclinical or discovery stages of development with no marketed drugs, reflecting hurdles such as achieving targeted delivery and minimising immunogenicity.
Since RFK Jr’s funding cuts primarily target mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases, investor interest may shift towards other applications of mRNA technology. Following the HHS announcement, the largest round of venture financing for mRNA-based drugs was received by US-based biotech Strand Therapeutics in August 2025, raising $153m in venture financing towards the development of its portfolio of mRNA-based drugs. The company’s lead drug, STX-001, is an interleukin-12-targeting mRNA-based therapy that is currently in Phase I/II trials for the treatment of solid tumours.
The Trump administration’s efforts to scale back federal support for mRNA-based vaccines could disrupt early-stage drug development, which relies on government support to de-risk research and development and attract subsequent private investment. In addition, government skepticism of mRNA technology, especially its use in vaccines for infectious diseases, could create investor uncertainty and lead to a downturn in venture financing for mRNA-based drugs. Future investment in mRNA-based drugs may increasingly favour biotech companies headquartered outside of the US, as well as shift away from US-based sources of capital. For further insights into the latest deal trends in the pharma sector, please see GlobalData’s Venture Capital Investment Trends in Pharma – Q2 2025 and M&A Trends in Pharma, Q2 2025 reports.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData