Sepsis is a life-threatening complication that arises from an infection, and occurs when the body’s response to the infection damages its tissues and organs. Sepsis can lead to multiple organ failure and death, especially if it is not recognised early and treated promptly. Although any type of infection (bacterial, viral, or fungal) can lead to sepsis, people suffering from pneumonia, abdominal infection, kidney infection, and bloodstream infection (bacteremia) are more likely to develop sepsis. The risk of sepsis is higher in an older population, where it is usually life-threatening as older individuals are more likely to suffer from multiple health conditions and have weakened immune systems.
GlobalData epidemiologists forecast that the diagnosed incident cases of sepsis in the seven major markets (7MM: US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK, and Japan) will grow at an Annual Growth Rate (AGR) of 2.06% per year over the next 10 years, from 2,594,665 cases in 2016 to 3,129,753 cases in 2026. The US will have the highest AGR at 2.34%, while Italy will have the lowest AGR at 0.82%. Of the 7MM, the US had the highest number of diagnosed incident cases of sepsis, with 2,005,428 cases in 2016, while Japan had the lowest number of diagnosed incident cases of sepsis, with 33,791 cases in 2016.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
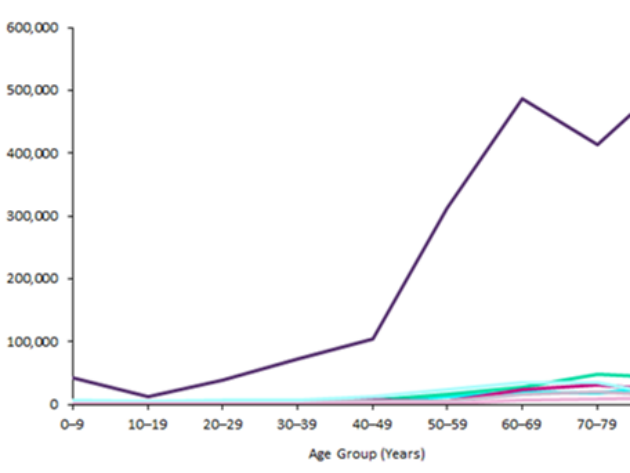
The diagnosed incident cases of sepsis consistently increase with age throughout the 7MM. In 2016, people aged 80 years and older made up the highest proportion (25.24%) of diagnosed incident cases of sepsis, followed by adults aged 60–69 years (23.67%). Children and adolescents aged 10–19 years accounted for the fewest diagnosed incident cases of sepsis (0.93%) in the 7MM in 2016. The US had a strong trend showing an increase in diagnosed incident cases of sepsis, especially after ages 40–49 years, whereas the rest of the 7MM showed a slight increase in diagnosed incident cases of sepsis from ages 50–59 years. Figure 1 presents the age-specific diagnosed incident cases of sepsis in the 7MM in 2016.
Figure 1: 7MM, Age-Specific Diagnosed Incident Cases of Sepsis, Both Sexes, All Ages, N, 2016

Sepsis is an extremely costly medical expenditure, whether it occurs during an initial hospital admission or it leads to a readmission. There could be many reasons for the increasing incidence of sepsis in an aging population. Older individuals are more likely to suffer from multiple health conditions, have weakened immune systems, or become infected by antibiotic-resistant bacteria that worsens their susceptibility to sepsis. GlobalData forecasts that death rates from sepsis are also set to increase over the next decade; this could be due to the growth in the aging global population and the resulting increasing incidence of sepsis. Hence, there is need to improve the early detection and management of sepsis and overall reduce sepsis death rates for patients admitted to the hospital.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData



