The biopharmaceutical industry had a positive year in 2024, with obesity drug developers continuing to witness success. 19 of the top 20 publicly traded global biopharmaceutical companies reported revenue growth, resulting in a more than 7.9% increase in total revenue, up to $880.4bn from 2023 to 2024, according to GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
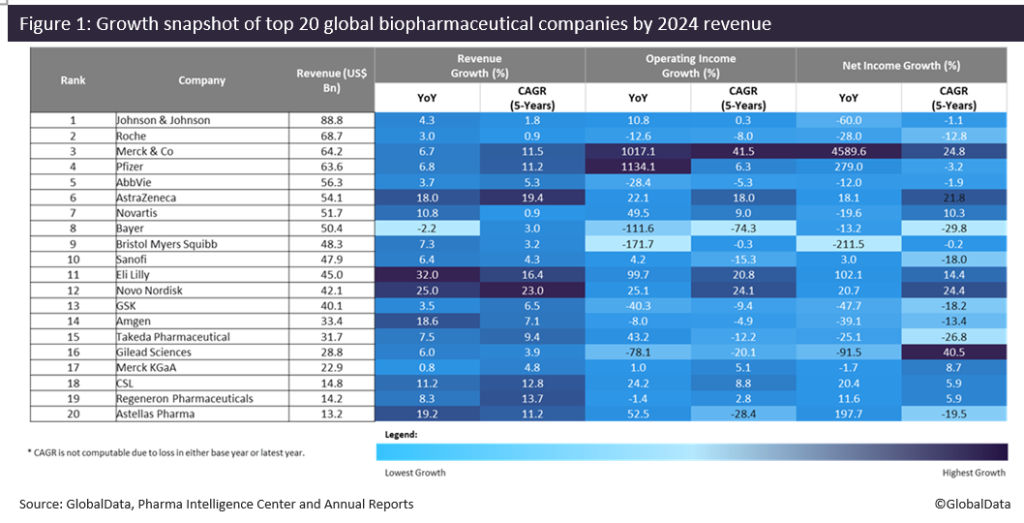
Eli Lilly experienced the highest revenue growth of 32% to $45bn in 2024, followed by Novo Nordisk with 25.5% to $42.1bn. This revenue growth was fuelled by the strong successes of the companies’ obesity and diabetes blockbuster drugs. Eli Lilly’s Mounjaro (tirzepatide) and Zepbound (tirzepatide) generated total global sales of $16.5 billion in 2024, while Novo Nordisk’s Ozempic (semaglutide) and Wegovy (semaglutide) amassed combined global sales of $25.9bn. Eli Lilly’s revenue growth was further driven by its breast cancer drug Verzenio (abemaciclib), which recorded global sales of $5.3bn in 2024. The revenue growth gap between the two companies is anticipated to widen as Eli Lilly’s Mounjaro and Zepbound continue to capture long-term market share from Novo Nordisk’s Ozempic and Wegovy. Eli Lilly is projected to see 34.3% revenue growth to $59.2bn in 2025, whereas Novo Nordisk’s is only forecast to see 16.4% revenue growth to $47.7bn in 2025, according to GlobalData’s Sales and Forecast database.
Astellas Pharma also demonstrated strong performance with 19.2% growth to $13.2bn, driven by the sales of Xtandi (enzalutamide) for prostate cancer, which registered global sales of $5.98bn in 2024.
Pfizer and Roche both witnessed a recovery in revenue after sales declines in the previous year, driven by waning demand for their Covid-19 products. Pfizer’s revenue grew 6.8% to $63.6bn in 2024, and Roche’s revenue grew 3% to $68.7bn in the same year. Pfizer’s Covid-19 antiviral treatment Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) saw an unprecedented 347% resurgence in sales to $5.7bn in 2024, spurred by strong demand in the US. However, Pfizer’s post-pandemic sales recovery is increasingly shifting towards its non-Covid-19 products, led by Eliquis (apixaban), which generated $13.3bn of global sales in 2024. The company is poised to see further revenue growth from its December 2023 acquisition of Seagen, with its marketed drugs Padcev (enfortumab vedotin), Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin), Tukysa (tucatinib), Tivdak (tisotumab vedotin) and Aidexi (disitamab vedotin) projected to achieve combined global sales of $8.8bn by 2031.
10 of the top 20 companies recorded above 10% year-on-year (YoY) growth in their operating profit in 2024: Pfizer (1,134.1%), Merck & Co (1,017.1%), Eli Lilly (99.7%) and Astellas Pharma (52.5%) reported more than 50% growth. Pfizer’s massive increase in its operating profit was attributed to ongoing cost-cutting initiatives which saved $4.5bn. Meanwhile, the strong success of Merck & Co’s Keytruda (pembrolizumab) led to a surge in its operating profit growth of 1,017.1%. It was further enhanced by lower royalty rates and reduced research and development (R&D) expenses. However, Bristol Myers Squibb (-171.7%), Bayer (-111.6%), and Gilead Sciences (-78.1%) reported more than a 50% decline in their operating profit.
Four players achieved above 100% growth in net profit during the year: Merck & Co (4,589%), Pfizer (279%), Astellas (197.7%) and Eli Lilly (102%). Merck & Co’s growth was primarily driven by its operating income, combined with the absence of legal settlement charges, which had impacted its net income in 2023 due to the Zetia antitrust case. An increase in gross margin primarily drove Eli Lilly’s growth.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData11 companies reported a YoY decline in profitability, with Bristol Myers Squibb (-211.5%), Gilead Sciences (-91.5%) and Johnson & Johnson (-60%) reporting a more than 50% decline. Bristol Myers Squibb and Gilead Sciences’ decreases in operating income by 171.7% and 78.1%, respectively, and their declines in net income by 211.5% and 91.5%, respectively, were primarily attributed to impairment charges and acquired in-process research and development expenses.
The top biopharmaceutical companies have witnessed a rebound in growth, with obesity drug developers continuing to reap success. Eli Lilly is poised to outpace Novo Nordisk in revenue growth over the next few years, capturing long-term market share from Novo Nordisk in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, companies that previously saw success with their Covid-19 products, such as Pfizer and Roche, are recovering from post-pandemic revenue losses through their diversified portfolios. However, the momentum in revenue growth is anticipated to slow in 2025 as the biopharmaceutical industry faces headwinds, including loss of exclusivity for major drugs and drug pricing pressures in the US.





