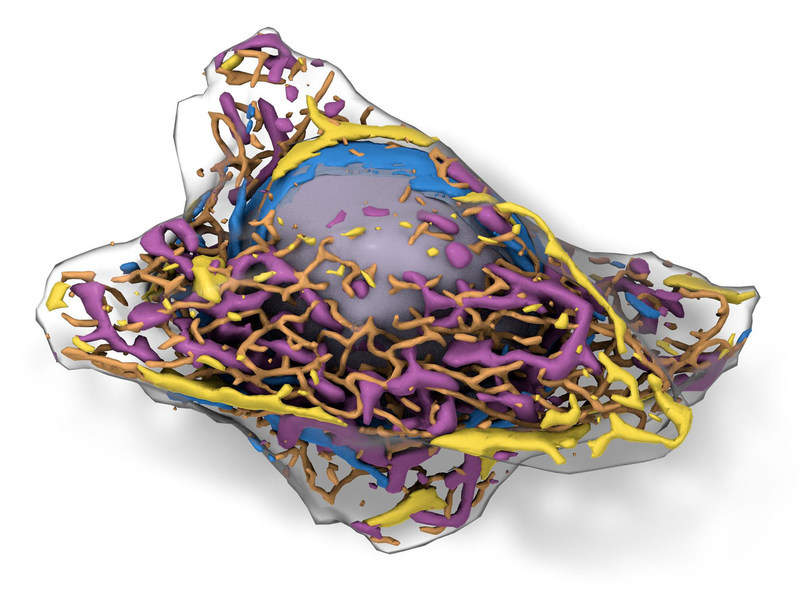
The Allen Institute for Cell Science in the US has developed a three-dimensional (3D) model that allows researchers to view various structures inside a living human cell.
The ‘predictive’ Allen Integrated Cell is made up of a large collection of living cells that have been gene edited to have fluorescent protein tags that illuminate specific cell structures such as the nucleus and mitochondria.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
Researchers imaged the tagged cells and used artificial intelligence to analyse the shape of cell structures and study their spatial relationships.
They then generated a probabilistic model that could accurately predict the shape and location of structures in any cell, based on the plasma membrane and shape of the nucleus.
Using another machine learning algorithm, information from cells with fluorescent labels was used to identify cellular structures in those without labels.
This 3D cell could pave way for better insights into cells and disease models.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataAllen Institute for Cell Science executive director Rick Horwitz said: “It’s like seeing the whole cell for the first time. In the future, this will impact drug discovery, disease research and how we frame basic studies involving human cells.”
The researchers believe the such label-free model could be used to capture brightfield microscope images to simultaneously and accurately picture the integration of different structures inside cells.
Allen Institute for Cell Science modeling director Molly Maleckar said: “Fluorescence microscopy is expensive and toxic to cells; increasingly so when you tag multiple structures.
“Our approach allows scientists to view cells and conduct experiments at the reduced cost of brightfield microscopy, with the structure-identifying power of fluorescence microscopy and without its toxic effects.”
The institute is also launching an online visual guide to human cells, an interactive overview of human cell structure and function.




