Dermatophytic onychomycosis (DO) is a form of chronic fungal infection of the nails caused by dermatophytes, a type of fungi that requires keratin for growth.
However, with less than 50% of cases being diagnosed in the US, the problem may be much worse than expected.
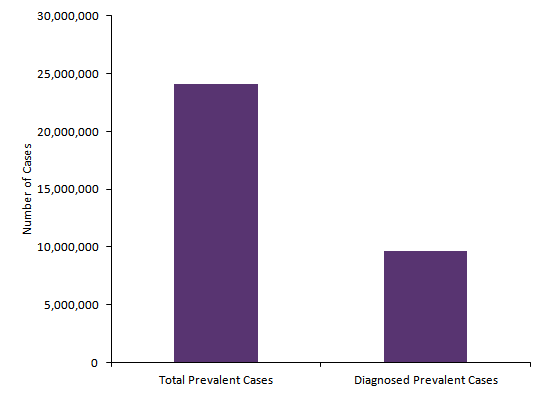
Figure 1 presents the estimated number of total prevalent (diagnosed and undiagnosed) cases of DO and the diagnosed cases of DO in men and women in the US in 2018.
Based on estimates from GlobalData, in 2018 there were more than 23.9 million total prevalent cases but only 10.5 million diagnosed prevalent cases of DO in the US. Of those, more than 85% were DO infections of the toe. This yields a diagnosis rate of around 40%, meaning that more than half of all cases of DO go undiagnosed and might be inadequately treated.
DO can occur in both fingernails and toenails; however, it is most commonly found affecting the toes and predominantly affects adults ages 30–60 years. Symptoms of this disease can include nail discolouration, thickening of the nail, splitting of the nail, separation of the nail from the nail bed, and overall discomfort in the affected area.
Diagnosis is made difficult by lack of consultations by those with the condition and the availability of over-the-counter treatments and can be complicated by misdiagnosis, as the disease may be confused for other conditions like nail psoriasis.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataAlthough numerous over-the-counter remedies exist for treating fungal foot infections, they may not suffice for DO. Without an accurate diagnosis, the condition may be difficult to adequately treat, leading to more severe symptoms and complications.